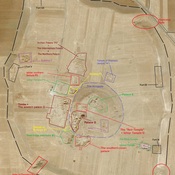
Il n'y a pas une annotation en français. Présenté est une annotation en Anglais.
Archaic Place P5 was built in the early second millenium BC -Ebla IIIA [Third Eblaite, first phase c. 2000 BC–c. 1800 BC].
Sources:
- Paolo Matthiae, Ebla and the early urbanization of Syria in: Joan Aruz, Ronald Wallenfels eds., Art of the First Cities: The Third Millennium B.C. from the Mediterranean to the Indus, New Metropolitan Museum of Art, 2003, p. 165nn
- http://www.ebla.it/escavi__il_palazzo_reale_g.html-Old Syrian Palaces
-
Peter M. M. G. Akkermans, Glenn M. Schwartz, The Archaeology of Syria: From Complex Hunter-Gatherers to Early Urban Societies (c.16,000-300 BC), Cambridge University Press, 2003, p.295 nnAstour, Michael C. (2002). "A Reconstruction of the History of Ebla (Part 2)". In Gordon, Cyrus Herzl; Rendsburg, Gary. Eblaitica: Essays on the Ebla Archives and Eblaite Language. 4. Eisenbrauns, p. 164
Archaic Place P5 was built in the early second millenium BC -Ebla IIIA [Third Eblaite, first phase c. 2000 BC–c. 1800 BC].
Sources:
- Paolo Matthiae, Ebla and the early urbanization of Syria in: Joan Aruz, Ronald Wallenfels eds., Art of the First Cities: The Third Millennium B.C. from the Mediterranean to the Indus, New Metropolitan Museum of Art, 2003, p. 165nn
- http://www.ebla.it/escavi__il_palazzo_reale_g.html-Old Syrian Palaces
-
Peter M. M. G. Akkermans, Glenn M. Schwartz, The Archaeology of Syria: From Complex Hunter-Gatherers to Early Urban Societies (c.16,000-300 BC), Cambridge University Press, 2003, p.295 nnAstour, Michael C. (2002). "A Reconstruction of the History of Ebla (Part 2)". In Gordon, Cyrus Herzl; Rendsburg, Gary. Eblaitica: Essays on the Ebla Archives and Eblaite Language. 4. Eisenbrauns, p. 164


.jpg)