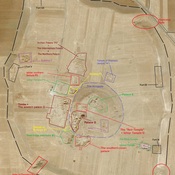
The monumental Temple of the Rock (Temple HH) in the Lower Town South-East erected in the Early Syrian period. According the textual evidencesanctuary was dedicated to the main Ebla god Kura1. The identification of the god Kura is not quite clear. One hypothesis is Kura was the hypostahasis of one of the main Mesopotamian gods i.e. Hadad or Dagan2
The temple was built during the Early Bronze IVA ca 2400 BC. and destructed ca 2300 BC.
- Paolo Matthiae, Ebla and the early urbanization of Syria in: Joan Aruz, Ronald Wallenfels eds., Art of the First Cities: The Third Millennium B.C. from the Mediterranean to the Indus, New Metropolitan Museum of Art, 2003, p. 165nn
- http://www.ebla.it/escavi__i_templi_paleosiriani.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ebla
- Maolo Matthiae, Recent Excavations at Ebla, 2006-2007 in: Proceedings of the 6th International Congress of the Archaeology of the Ancient Near East: Excavations, surveys and restorations : reports on recent field archaeology in the Near East, Otto Harrassowitz Verlag, 2010 p. 6 nn
- Paolo Matthiae, Rbla. Recent Excavation Results and the Continuity of Syrian Arts in: Cultures in Contact: From Mesopotamia to the Mediterranean in the Second Millennium B.C, Cultures in Contact: From Mesopotamia to the Mediterranean in the Second Millennium B.C. 2013, pp. 96-111
- Maria C. Biga, "Inherited Space – Third Millennium Political and Cultural Landscape", in: Eva Cancik-Kirschbaum, Nicole Brisch and Jesper Eidem (Eds.), Constituent, Confederate, and Conquered Space in Upper Mesopotamia. The Emergence of the Mittani State, Berlin, Boston: De Gruyter, 2014, 93–110
References
- ↑Maolo Matthiae, Recent Excavations at Ebla, 2006-2007 in: Proceedings of the 6th International Congress of the Archaeology of the Ancient Near East: Excavations, surveys and restorations : reports on recent field archaeology in the Near East, Otto Harrassowitz Verlag, 2010 p. 6
- ↑Maria C. Biga, "Inherited Space – Third Millennium Political and Cultural Landscape", in: Eva Cancik-Kirschbaum, Nicole Brisch and Jesper Eidem (Eds.), Constituent, Confederate, and Conquered Space in Upper Mesopotamia. The Emergence of the Mittani State, Berlin, Boston: De Gruyter, 2014, 93–110










.jpg)



.jpg)